RAID 5 vs RAID 6
This article focuses on the topic of Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks (RAID) and focuses in more detail on RAID 5 vs RAID 6. This storage virtualization technology combines multiple physical disk components into one or more logical blocks to provide data redundancy and performance.
Each RAID level is used for a specific purpose, so knowing the features of each array will help you choose the array that is right for you. such as RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 2, RAID 3, RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10. Many users compare RAID 5 vs RAID 6 to find the right array for their storage, so this post will focus on RAID 5 vs RAID 6.
You will be able to learn the main characteristics of RAID 5 vs RAID 6, as well as their main differences, then you will have a complete understanding of the two levels of RAID. You will also learn how to protect each file on your array as much as possible and how to repair damaged arrays if necessary. It will be interesting, let's get started!
Article content:
- About RAID 5
- About RAID 6
- RAID 5 vs RAID 6
- How to recover lost RAID data
About RAID 5
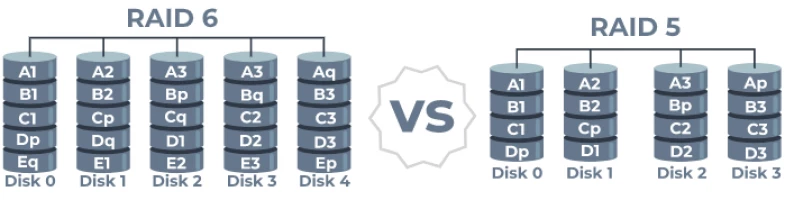
RAID 5 uses block-level striping with distributed parity, and the parity information in RAID 5 is distributed across drives, which is different from RAID 4. So if one drive fails, subsequent reads will be distributed parity, therefore, no data is lost.
To create such an array, you need to prepare 3 or more disks, while rebuilding the array requires all disks, which can lead to disk failure or loss of the entire array.
The main advantages of RAID 5:
- Recovery of a failed drive occurs in a short time.
- RAID 5 makes efficient use of the available space.
- High reading speed.
- There is data redundancy.
- This array configuration is stable and reasonably reliable.
- A swappable drive is available to prevent downtime.
Main disadvantages of RAID 5:
- This RAID cannot handle two simultaneous hard drive failures.
- The write speed is relatively low.
- Restoring data can take a long time and is somewhat difficult to accomplish.
About RAID 6
RAID 6 uses block-level striping with double distributed parity. Double parity makes RAID 6 not only fault-tolerant, but also attractive for high-availability systems.
To create a RAID 6, you will need 4 or more disks, so this option will be more expensive.
The main advantages of RAID 6:
- It has high redundancy and fault tolerance, and this allows you to perform operations at an acceptable speed.
- Data Availability and security are also at a high level.
- Two drive failures can be repaired.
Main disadvantages of RAID 6:
- Write speed is slow.
- The implementation of this array is complex and expensive.
- The recovery process will take a long time.
RAID 5 vs RAID 6
RAID 5 vs RAID 6 are defined in the preceding information. You may also have a working knowledge of the two RAID levels. Let's look at the distinctions between RAID 5 vs RAID 6.
In terms of fault tolerance, performance (including write and read performance), capacity utilization, application, and hardware or software RAID, the distinctions will be described.
RAID 5 VS RAID 6: Fault Tolerance
For the sake of data security, fault tolerance is essential. If one of the RAIDs is fault-tolerant, you won't lose data if one of the hard drives fails. If it isn't, you should create a Windows backup in case of system failure. The RAID 5 can withstand a single-drive failure, implying that the RAID 5 can continue to function even if one of the hard drives fails.
However, if two or more disks fail, you will lose your data. RAID 6 can withstand up to two hard disk failures. As a result, RAID 6 is more fault tolerant than RAID 5.
Which one wins between RAID 6 and RAID 5? RAID 6 is the winner in terms of failure tolerance.
RAID 5 VS RAID 6: Performance
The performance of a hard disk is essential, and RAIDs are no exception. What about RAID 5 vs RAID 6 performance? When it comes to hard disk performance, there are two key elements to consider (write performance and read performance).
In fact, a RAID 5's read performance is fairly similar to that of a RAID 6. However, because of the additional parity information that must be generated, RAID 6's write performance is somewhat slower than RAID 5.
RAID 5 VS RAID 6: Capacity Utilization
If one drive's capacity utilization is higher, you may store more data on it. As a result, this is a crucial consideration when selecting a drive. Which option has a higher capacity utilization rate? Which is better: RAID 5 vs RAID 6?
According to research, RAID 5 capacity usage varies from 67 percent to 94 percent, while RAID 6 capacity utilization ranges from 50 percent to 88 percent. RAID 5 is clearly superior in terms of capacity. Which is better: RAID 5 vs RAID 6? RAID 5 wins in terms of capacity utilization rate.
RAID 5 VS RAID 6: Application
The distinction between RAID 5 vs RAID 6 may also be seen in the applications. They have many applications in life depending on their qualities. RAID 5 is commonly used in data warehousing, web serving, and archiving, for example.
RAID 6 is generally used for data archiving, disk backups, high-availability solutions, and servers with enormous storage needs. As you can see, RAID 6 has a wide range of applications. So, which is better: RAID 5 vs RAID 6? You have the option of making a selection based on your requirements.
RAID 5 VS RAID 6: Software or Hardware RAID
One difference between RAID 5 vs RAID 6 is the software/hardware RAID setup. In general, a software RAID does not necessitate RAID hardware, but a hardware RAID requires. When it comes to RAID 6 versus RAID 5, you can set up a RAID 5 array using either software or hardware RAID. However, you'll need a hardware RAID to create a RAID 6 array.
Recover your Lost Data Using DiskInternals RAID Recovery
Rest easy and don't worry about losing array data. You should immediately download and install the professional DiskInternals RAID Recovery utility, and here's why: this application can repair corrupted RAIDs both automatically and manually, so the DiskInternals team strives to make the recovery process simple and fast. This leading application has been improved and modernized by leading IT specialists for 16 years.
DiskInternals RAID Recovery is designed to restore software and hardware RAIDs.
As mentioned above, there are options for manual and automatic recovery, while automatic recovery includes a step-by-step recovery wizard. The recovered files and folders are exported to local or remote locations, this application also supports Unicode filenames and layered folders. You can use DiskInternals RAID Recovery to create a disk image, then you can protect your data from being lost in the future, you never know what might happen.
It should be noted that the application recovers data from badly damaged pools that are no longer mounted and automatically determines the pool and file system parameters, including the disk order.
The utility works even if a new empty pool was created over the original one and at the same time perfectly restores deleted files; restores previous versions of files whenever possible and verifies checksums to make sure the file data is correct!
Here is how to use the recommended application to protect the array:
Step 1: Turn off the computer/server and disconnect the drives that make up the RAID 5 or 6 array.
Step 2: Connect these drives consistently and carefully to a running computer (after turning off the power).
Step 3: Turn on a working computer. Then download and install RAID Recovery from the site and rest easy without worrying about data loss.
Step 4: Open the application and run the Recovery Wizard (then there will be automatic data recovery), or switch to full manual control of the application (if you have enough experience).
Step 5: RAID Recovery automatically detects available attached arrays - select the one you want and then select the desired recovery mode. Be patient, as the process of rebuilding the array will most likely take a long time, and this is normal, because the recovery volumes of RAID 5 or 6 are enormous here.
Step 6: After scanning, the results will appear on the monitor screen - view them for free, and then complete this whole process by purchasing a license and saving the data. Don't worry, buying a license won't take your precious time - it's a matter of a few minutes.
Recovery tips:
- When choosing a drive for quick scan, select the correct drive; otherwise you won't be able to find your files.
- Take your time and be patient until each step is done according to the standards.
- Review all data before restoring it to a safe place.
- Do not save data again on the same disk, as this may overwrite the data.
RAID 5 VS RAID 6: Capacity Utilization
If one drive is better at utilizing capacity than another drive, it can store more data - that's proven, so it's also an important consideration when choosing a drive.
Based on research, RAID 5 capacity utilization ranges from 65% to 94%, and RAID 6 ranges from 50% to 87%, so it can be concluded that RAID 5 has the best capacity. So, in terms of capacity utilization, RAID 5 still wins.
RAID 5 VS RAID 6: Application
These arrays have different applications in life. So, RAID 5 is mainly used for web serving, data storage and archiving.
RAID 6 is mainly used for data archiving, backup to disk. In addition, it offers high availability solutions and servers with large capacity requirements.
As you can see, RAID 6 has a wider application.
RAID 5 VS RAID 6: Software or Hardware RAID
Software RAID does not require hardware RAID, but hardware RAID does. As for RAID 5, you can set up either software or hardware RAID for a RAID 5 array. To create a RAID 6 array, you need hardware RAID, which is probably more expensive.
Frequently asked questions
1. What to choose: RAID 5 vs. RAID 6?
The decision depends on your preference: if you want high capacity utilization, RAID 5 is better, if you want higher fault tolerance, you should choose RAID 6.
2. Which RAID should you choose?
For SMBs, RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10 are good enough to meet user needs. If you are on a budget, both RAID 5 vs RAID 6 will do. Of course, for large data centers, RAID 10 will provide the most benefits.
3. Which RAID is best for performance?
It is likely that RAID 5 is better suited for performance and redundancy than other options. In addition, it can provide a wide range of disk usage and strong data protection.
4. What About RAID 6 Fault Tolerance?
If the array consists of four drives, two drives will be used to store each block of data, and the other two will be used to store parity blocks, so you will lose a maximum of 2 drives at a time without data loss.
Conclusion
You may have already decided which option is better than RAID 5 vs RAID 6. In any case, you won't have to worry about your information, as DiskInternals RAID Recovery is the leader in protecting data of any format and size.