RAID 0 vs RAID 1: which one to choose?
RAID0 and RAID1 are two different types of RAID arrays. If you mistakenly deleted your important files from a RAID0 or RAID1 volume, this article explains how DiskInternals RAID Recovery software can help you get back the lost file(s).
Article content:
- RAID 0 vs RAID 1 comparison
- RAID 0 and RAID 1 differences
- Which one to choose?
- How DiskInternals RAID Recovery may be useful?
- How to recover lost RAID data
What is RAID 0
Also referred to as “Disk Stripping,” RAID 0 is a technology that allows you to combine two drives into one. For example, you can combine a 500 GB HDD with a 250 GB HDD to become a single 750 GB drive. With RAID 0, data can be written across multiple disks at the same time.
RAID 0 typically increases a PC's performance because more disks are handling the read and write process. However, one of the biggest disadvantages of RAID 0 is that it doesn't have fault tolerance and parity information redundancy. So to say, if one of the RAID 0 disks fail, you'd lose the entire array - along with your files.
Key Features:
- Speeds up read and write operations
- Strips volume without fault tolerance
- No parity disk
- Budget-friendly
Notes About Striping:
- Triggers an increase in performance but does not provide fault tolerance; so, one disk failure would lead to a fatal data loss.
- Stripe sets are more open to data loss than saving your files on a single spindle.
- Minimum 2 disks are required.
- Stores data in chunks and strips it across the RAID array.
- It is the fastest RAID disk array.
What Is RAID 1
RAID 1 is a standard RAID array that mirrors the data on two or more disks. To achieve this RAID array, you need at least two disks; RAID 1 saves a copy of the same data on the connected disks. Unlike RAID 0, this array provides fault tolerance and redundancy.
So, it is easy to recover data from RAID 1 arrays, because you can always access the data from any of the disks that are still working fine. When creating a RAID 1 array, you should ensure that the array is as big (in size) as the smallest disk because data is mirrored on all disks in the array.
Key Features:
- Two or more disks can be used.
- Provides fault tolerance in case one of the drives fail
- No parity.
- High data security.
- Costlier than RAID 0.
Notes About Mirroring:
- Mirrored volumes copy data into all the disks in an array; so, when one disk fails, the system switches to another disk, and all the data would still be accessible.
- Mirroring provides fault tolerance, whereby your data is still available even after a disk failure.
- Does not improve performance.
- Half of the array disks are occupied by copied content from the original disk.
- RAID 1 array is the most expensive fault-tolerant system.
RAID 0 and RAID 1: Differences
There are pretty many differences between RAID 0 and RAID 1 arrays you need to know.
1. Performance:
RAID 0 boosts performance because it is structured to optimize desktop applications. With RAID 0 array, you’d most definitely achieve better performance than using a single drive.
On the other hand, RAID 1 provides better read performance using a single disk. However, if you set up different HDDs or SSDs with different speeds, the speed of your RAID 1 array would be equal to the speed of the slowest disk.
2. Reliability:
Your data and important files are at high risk with RAID 0 because it does not provide fault tolerance and redundancy. To keep your files safe in a RAID 0 array, you need to always back it up. In contrast, RAID 1 provides fault tolerance and redundancy, and as such, your files are safer in this array.
3. Data Organization
RAID 0 array supports data stripping without mirroring and parity, which implies to say that data would be split across the connected disks. RAID 1 supports mirroring; so, data is saved evenly on each disk on the array. So, both RAID 0 and RAID 1 offer good data organization, but you'd be safer with RAID 1 since it provides fault tolerance.
4. Storage Capacity
Apparently, you'd get more storage capacity with RAID 0 because it doesn't support redundancy. In RAID 0, the total storage you've got is the sum of all integrated individual disk capacities. In contrast, in RAID 1 arrays, the total storage capacity is equal to just one disk's capacity - the original disk.
Which One to Choose?
Between RAID 0 and RAID 1, which one is the "perfect" one for you to choose? Well, many factors would guide your decision and selection. Both arrays are unique in different ways, and they have their advantages over one another. Choosing between RAID 0 and RAID 1 would base on your storage need and preference.
However, from a general perspective, if you need more security, flexibility, and the ability to gain access to your files even when one disk in the array fails, then RAID 1 is an ideal option to choose here.
In contrast, if you're more interested in speed, more storage space, and an increase in performance, RAID 0 is ideal. Typically, RAID 0 would work for heavy PC gamers because it provides faster write speed and more storage capacity.
How DiskInternals RAID Recovery May Be Useful?
The DiskInternals RAID Recovery software is a professional tool for data recovery. This program is built for Windows operating system and recovers both software and hardware RAIDs.
To make the recovery process smoother and easier, DiskInternals RAID Recovery integrates a Recovery Wizard that guides the user through the steps of data recovery. With this RAID recovery solution, you can retrieve all your lost files from RAID-6 arrays, and it is simply intuitive.
Furthermore, DiskInternals RAID Recovery supports Unicode filenames and multi-level folders. You can create multiple disk images for free, which would serve as backup copies for your important files in the case of data loss. To ensure effective recovery, DiskInternals RAID Recovery bypasses Windows restrictions during the recovery process.
How to Recover Lost RAID Data?
Simply, you need a RAID Recovery software program to help out - that's where DiskInternals RAID Recovery comes in. DiskInternals RAID Recovery can retrieve data from RAID 0 to RAID 6 arrays. It is a comprehensive solution for recovering data from advanced file systems and virtual disk volumes.
This software can recover both hardware and software RAID and goes on to integrate all features of Partition Recovery. Furthermore, DiskInternals RAID Recovery can get back lost files from MegaRAID, Silicon RAID Controllers, and DDF-compatible devices.
Recovering data with this program is quite easy; either you do it manually or follow the step-by-step guide provided by the built-in Recovery Wizard.
Steps to Use DiskInternals RAID Recovery
The process is straightforward and fast; even a non-IT professional can use this recovery program without needing 3rd-party assistance.
First Step:
Download and install RAID Recovery on the Windows OS system. This software is compatible with Windows 7/8/8.0/10/-11 and Windows Server 2003-2019.
Second Step:
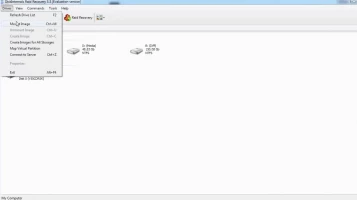
Launch the app after installation and select the affected target array. Next, choose a recovery mode:
- Fast recovery mode
- Full recovery mode
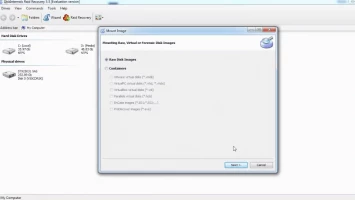
The Fast Recovery Mode scans very fast and saves time, but it doesn’t get deeper to discover all the lost files. Full Recovery Mode takes time and retrieves all lost files.
Third Step:
DiskInternals RAID Recovery would automatically check the status of the selected RAID array, controller, file system, or disk to recover lost files. You can preview the recovered files before proceeding to save them back to your local storage. To save the recovered files, you need to purchase a license.
Is the damage too deep/severe for you to restore? You can request guided assistance from RAID Recovery experts.
Recovery tips:
- Follow the recovery steps diligently - wait until each step executes successfully before proceeding to the next; don’t hurry!
- Make sure you select the right drive for the scan; else, the program won't find the file(s) you want to recover.
- Preview the files before attempting final recovery.
- Don't re-save the recovered data on the same drive where it was deleted/lost.
Video Guide On RAID Data Recovery Process
Here’s a video guide to clarify the entire steps explained above; watch to understand better:
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is RAID 0 faster than a single disk?
Yes, RAID 0 offers more speed and improved performance than a single disk because data is split across all disks - more disks in the array equals more speed.
2. Can You Use Different Drives on RAID 0?
Yes, you can add HDDs or different sizes. The storage capacity you’d get is the total storage capacity of all connected HDDs.
3. Can You Use SSDs for RAID 0?
RAID 0 requires 2 or more disks; the disks could be HDDs or SSDs. So, you can use 2 SSDs for RAID 0.
Conclusion
RAID 0 vs RAID 1 is a comparison of speed vs fault tolerance. With RAID 0 you’d get more speed, with RAID 1 you’d get more security (fault tolerance). Regardless, with DiskInternals RAID Recovery, you can get back files lost from either RAID 0 or RAID 1 arrays.
RAID 0 does not provide fault tolerance, so, failure of one disk means you’d lose all your data in the array. However, it provides more speed and storage capacity than RAID 1. With RAID 1, you’d have more data security but less storage capacity. Choosing between these two RAID arrays would base on your need and preference.